Leave your message now to get your free sample and discount price
Leave your message now to get your free sample and discount price
Cemented Carbide Tools have become a popular choice in machining due to their exceptional durability and performance. Machinists often seek tools that withstand wear and tear. Cemented carbide offers a solution, proving to be both tough and reliable. These tools have a high resistance to abrasion, making them ideal for various materials.
Using cemented carbide can enhance precision in machining. The sharp edges of these tools ensure cleaner cuts and finer finishes. However, not all machinists fully appreciate their potential. Some might overlook the importance of tool selection. Utilizing lower quality options occasionally leads to unsatisfactory results and costly rework.
Reflecting on the choice of tools can be crucial. Investing in high-quality cemented carbide tools pays off in the long run. Despite the initial cost, the longevity and efficiency they offer are significant advantages. Choosing the right tools shapes your machining outcomes, making it essential to consider these factors.
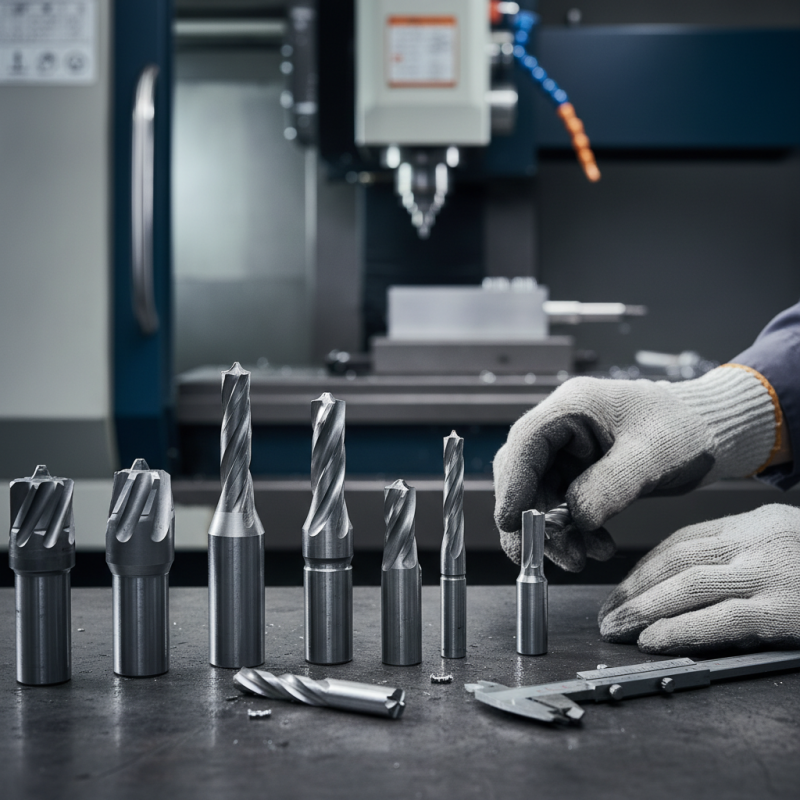

Cemented carbide tools are crucial in modern machining. They consist mainly of tungsten carbide grains bonded with a metal binder. This combination results in exceptional hardness and wear resistance. The metal binder is typically cobalt, which enhances toughness. The microstructure contributes to the tool's performance in demanding applications.
When choosing these tools, consider their composition carefully. Hardness is vital, but so is toughness. A balance between the two ensures durability. Not all cemented carbide tools perform equally. Some may chip or wear faster. Evaluating specific applications can lead to better decisions.
**Tip:** Always check the tool's specific carbide grade. Different grades suit various materials and processes.
Another point to reflect on is coatings. Coatings can further enhance the tool's performance. However, they may add to costs. Sometimes simpler, uncoated tools can be effective.
**Tip:** Consider starting with uncoated tools for basic tasks. This can help you assess the material's behavior without overspending.
| Properties | Cemented Carbide | High-Speed Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | Very High (HRA 90-95) | Moderate (HRA 60-65) |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Toughness | Moderate | High |
| Heat Resistance | High | Medium |
| Applications | Machining hard materials, precision tools | General machining, less demanding applications |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
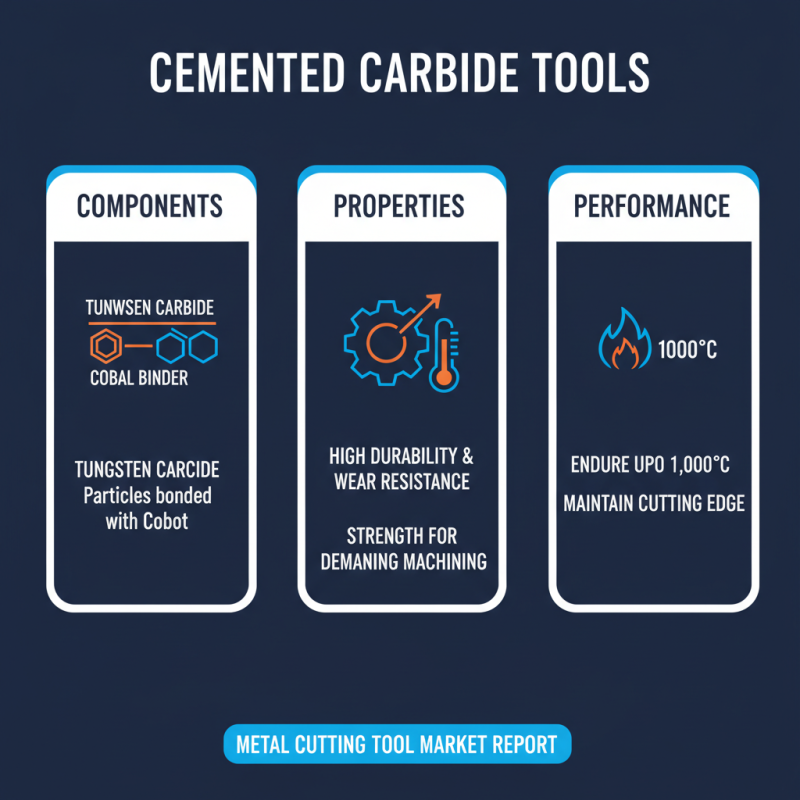
Cemented carbide tools are known for their high durability and wear resistance. These tools often consist of tungsten carbide particles, bonded with cobalt. This combination provides strength, crucial for demanding machining processes. A recent report from the Metal Cutting Tool Market indicated that cemented carbide tools can endure temperatures up to 1,000°C without losing their cutting edge.
One significant advantage of cemented carbide is its versatility. It can be used for various materials, including hardened steels and non-ferrous metals. This makes it a preferred choice in industries like aerospace and automotive. Statistics show that tools made from cemented carbide can last up to five times longer than high-speed steel tools. However, the higher initial cost can be a drawback for some manufacturers.
Moreover, the machining process can generate vibrations. These vibrations can affect precision. While cemented carbide tools are robust, proper handling and maintenance are essential. The tools can chip under excessive pressure or impact. Users must remain vigilant to get the best performance from these cutting tools.
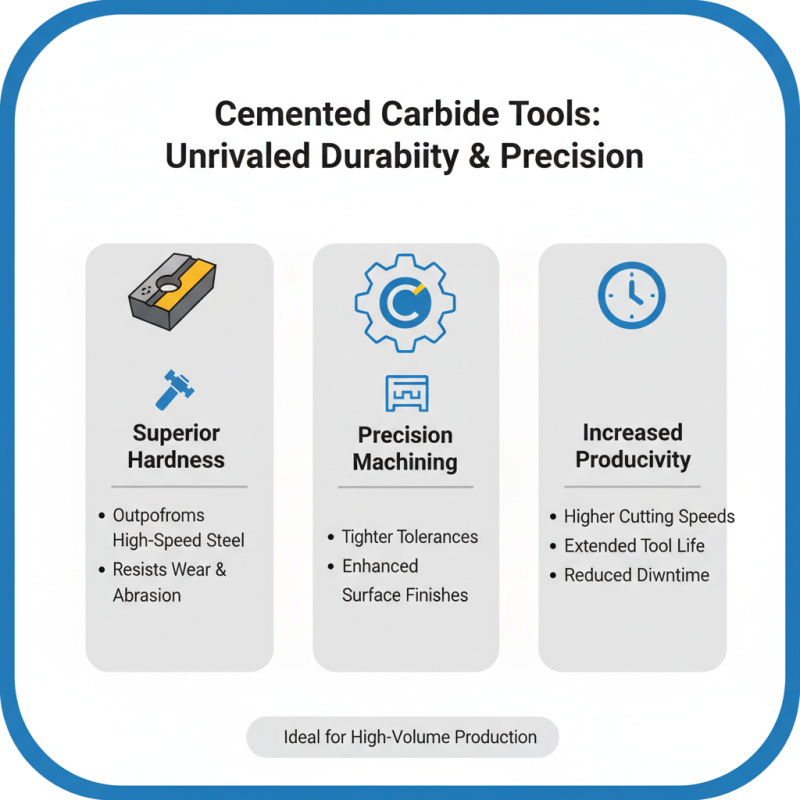
Cemented carbide tools stand out for their durability. They offer superior hardness compared to materials like high-speed steel or carbon steel. This hardness allows for precise machining, resulting in better surface finishes. While high-speed steel can handle lower speeds, cemented carbide excels under high production demands. It can maintain sharpness longer, reducing downtime for tool changes.
However, cemented carbide isn’t without drawbacks. Its brittleness can lead to chipping under stress. This is something manufacturers need to consider. In contrast, other materials may provide flexibility but at the cost of wear resistance. Carbon steel tools may bend, while cemented carbide may fracture if not used properly. Users must reflect on application requirements before making a choice.
Overall, analyzing performance is essential. Different materials serve unique purposes in machining. Weighing factors such as cost, durability, and application is vital. Sometimes, the best tool isn't always the most expensive one. Balancing quality and cost-effectiveness can lead to better production outcomes. Skilled machinists often know the value of experimenting with different materials for challenging jobs.
Cemented carbide tools are widely used across various industries due to their unique properties. They excel in high-performance machining tasks. According to a report from MarketsandMarkets, the global cemented carbide market is expected to reach $30.2 billion by 2026. This growth reflects the increasing demand for durable cutting tools.
In the automotive industry, cemented carbide tools are essential for manufacturing intricate parts. They offer superior wear resistance, resulting in longer tool life and reduced downtime. The aerospace sector also relies heavily on these tools for precision work, especially in components that require tight tolerances. However, challenges remain. The high cost of these tools can deter some manufacturers. Ensuring optimal usage is vital to maximize the return on investment.
Moreover, the mining industry benefits significantly from cemented carbide. Drilling tools made from this material can withstand extreme conditions. These tools enhance productivity but sometimes lead to increased environmental concerns. The manufacturing process of cemented carbide can produce hazardous waste, raising questions about sustainability. Addressing these issues is crucial for the future of machining industries.
Cemented carbide tools offer exceptional durability and performance, but they require proper maintenance to maximize their lifespan. Regular cleaning is vital. Dust and debris can accumulate and affect cutting efficiency. Using a soft brush or compressed air can help maintain their condition.
Moreover, proper storage is crucial for preventing damage to the cutting edges. Tools should be stored in a dry, clean environment. Humidity can lead to rust or corrosion. According to industry reports, improper storage can reduce tool life by up to 20%. That's a significant loss.
Additionally, tool inspection should be a routine practice. Check for signs of wear, chipping, or unusual patterns in cutting. Even minor surface damage can lead to larger issues. Data indicates that about 30% of tool failures stem from neglecting regular check-ups. A proactive approach saves time and resources in the long run.
This chart compares the tool life of different tool materials used in machining, emphasizing the superior longevity of cemented carbide tools.






