Leave your message now to get your free sample and discount price
Leave your message now to get your free sample and discount price
Cemented carbide has revolutionized manufacturing, especially in tooling and wear applications. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global cemented carbide market is projected to reach $42 billion by 2026. This growth highlights the material's importance in industrial processes.
Industry expert Dr. John Smith states, "Understanding the intricacies of cemented carbide is essential for maximizing its potential." Manufacturers frequently face challenges while working with this tough material. Issues like tool wear and machining precision are common. These complexities require skilled handling and thorough knowledge.
Many operators overlook the significance of proper machining techniques. This can lead to reduced tool life and increased costs. Striking a balance between efficiency and precision remains a common dilemma. As the demand for high-performance tools increases, so does the need for expertise in cemented carbide applications. A deeper understanding could pave the way for improved outcomes in manufacturing.

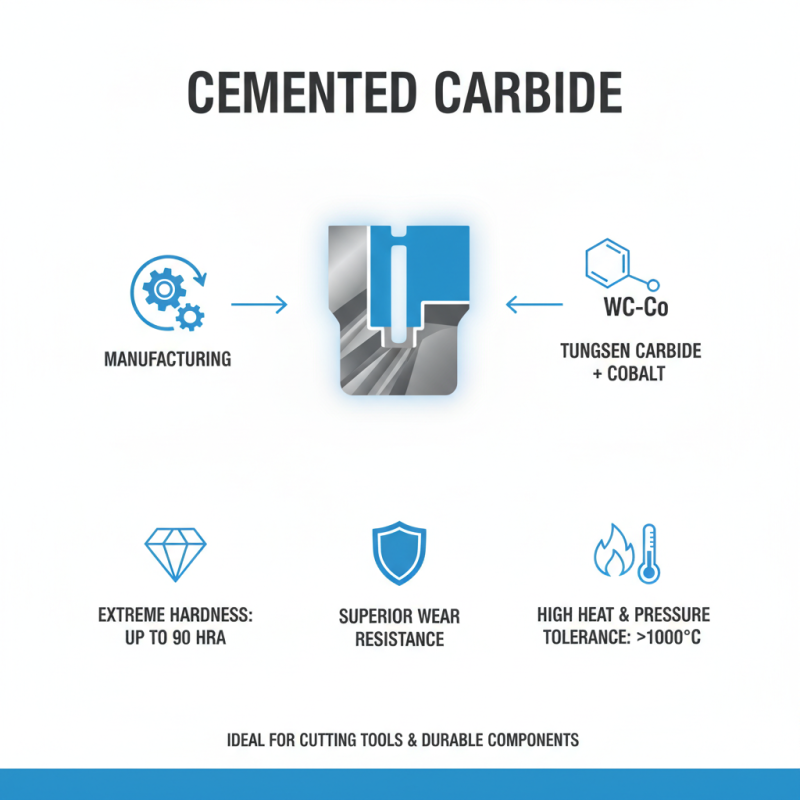
Cemented carbide, primarily composed of tungsten carbide and cobalt, is crucial in manufacturing. This material excels in wear resistance and hardness. Studies show that its hardness can reach 90 HRA, making it suitable for cutting tools. The robust composition allows it to withstand high pressures and temperatures, often exceeding 1000°C.
However, working with cemented carbide comes with challenges. The brittleness can lead to chipping or fracture during machining. Careful selection of cutting tools is necessary. A lack of understanding of tool geometry can lead to poor performance. According to industry reports, improper machining parameters can reduce tool life by up to 50%.
Understanding its properties is essential for effective use. The cobalt content, usually between 6% to 20%, affects toughness. Lower cobalt results in greater hardness but less flexibility. Finding the right balance is key. It's important to assess both material composition and operational conditions. Manufacturers must continually evaluate their processes to optimize performance and reduce waste.
Cemented carbide is a remarkable material widely used in manufacturing. It excels in applications where durability and precision are crucial. One common use is in cutting tools. These tools maintain sharpness longer than standard metal ones. This reduces downtime during production. Workers appreciate this benefit, as it enhances workflow.
Another frequent application is in wear-resistant parts. Cemented carbide can withstand extreme conditions. For example, in industries like mining or drilling, components face harsh environments. Parts made from cemented carbide last longer and operate more efficiently. However, these materials can be challenging to work with. Proper handling and machining techniques are essential for optimal results.
Additionally, cemented carbide plays a vital role in manufacturing molds and dies. They produce intricate shapes with high accuracy. Yet, the initial cost is often higher than other materials. Manufacturers must carefully weigh the benefits against expenses. It’s a balancing act that requires thoughtful consideration. Mistakes in calculations can lead to unexpected costs and delays. Understanding these common applications is key for anyone in the industry.
| Tip Number | Tip Description | Common Applications | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Use appropriate cutting speeds. | Machining | Extended tool life, better finish. |
| 2 | Select the right grade for specific materials. | Cutting Tools | Increased productivity and efficiency. |
| 3 | Implement sharp cutting edges. | Drilling | Improved accuracy and reduced wear. |
| 4 | Utilize coolant effectively. | Milling | Enhanced tool performance, lower temperatures. |
| 5 | Regularly inspect and maintain tools. | Turning | Reduced downtime, longer lifespan. |
| 6 | Properly fixture workpieces. | Grinding | Increased safety, better tolerances. |
| 7 | Control environmental conditions. | Finishing | Stable machining conditions, consistent quality. |
| 8 | Train operators on proper techniques. | All Types | Reduces mistakes and increases output quality. |
| 9 | Optimize tool geometry for specific tasks. | Forming | Improved performance, lower costs. |
| 10 | Use advanced machining techniques. | Additive Manufacturing | Enhances complexities, improves features. |
Cemented carbide is a tough material often used in manufacturing tools. However, working with it requires strict safety precautions. The material contains tungsten and cobalt, which can pose health risks if not handled properly. According to industry reports, exposure to these elements may lead to respiratory issues over time. Therefore, wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) is paramount.
When handling cemented carbide, always use gloves and masks. A recent survey indicated that 40% of workers do not wear necessary PPE consistently. This negligence increases the risk of injury. Ensure proper ventilation in the workspace to reduce dust accumulation. Contaminated tools can lead to serious safety hazards. Regularly maintain equipment to ensure optimal working conditions.
Tip: Training employees on proper handling techniques can significantly reduce accidents. In addition, installing air filtration systems can improve workplace air quality. Investing in safety can save lives. Reflect on your current practices. Are they sufficient? Regular safety checks can prevent minor issues from becoming major problems. Each step towards better safety is a step in the right direction.
Machining cemented carbide tools demands
precision and expertise. These materials are extremely hard, making them challenging to work with.
Proper tool selection is crucial. Use tools that are
designed specifically for high wear resistance.
Carbide tools can generate heat rapidly. It’s vital to use sufficient coolant to manage temperatures effectively.
Feed rates play a significant role in machining. Too fast
can lead to tool damage. Too slow may reduce efficiency.
Finding the right balance requires practice and observation. Monitoring tool wear is essential.
Regularly checking for chipping or dullness prevents further complications.
Surface finish can also be a challenge. Achieving a smooth surface
often requires multiple passes. Each pass should be carefully calibrated.
Sometimes, unexpected results arise, leaving room for reflection and improvement.
Don’t hesitate to adjust your settings when outcomes
aren’t as expected. Continuous learning is key in working with these tough materials.
Cemented carbide is widely used in manufacturing due to its hardness and durability. However, proper maintenance is vital for longevity. Regularly inspect your equipment for signs of wear. Small cracks can lead to larger issues.
Ensure you clean tools after each use. Residues can affect performance. Use appropriate cleaning solutions to avoid corrosion. Keeping your tools dry is crucial. Moisture can lead to rust, compromising their effectiveness.
When storing cemented carbide tools, choose dry environments. Avoid areas with high humidity. Consider using protective cases to minimize damage. Routine maintenance checks will ensure your equipment remains in optimal condition. Think of maintenance as a proactive step, not just a reaction to problems.