Leave your message now to get your free sample and discount price
Leave your message now to get your free sample and discount price
 Cemented carbide inserts play a pivotal role in modern manufacturing, revolutionizing the way machining processes are conducted across various industries. Constructed from a composite of carbide particles and a metal binder, these inserts are renowned for their durability, wear resistance, and exceptional cutting performance. As the demand for precision machining increases, understanding the characteristics and applications of cemented carbide inserts becomes essential for manufacturers looking to enhance productivity and quality. This introduction will delve into the significance of cemented carbide inserts in contemporary manufacturing, exploring their diverse applications ranging from metal cutting to woodworking. By examining the advantages these materials offer, we can better appreciate their crucial contribution to advancing manufacturing technologies in today's competitive landscape.
Cemented carbide inserts play a pivotal role in modern manufacturing, revolutionizing the way machining processes are conducted across various industries. Constructed from a composite of carbide particles and a metal binder, these inserts are renowned for their durability, wear resistance, and exceptional cutting performance. As the demand for precision machining increases, understanding the characteristics and applications of cemented carbide inserts becomes essential for manufacturers looking to enhance productivity and quality. This introduction will delve into the significance of cemented carbide inserts in contemporary manufacturing, exploring their diverse applications ranging from metal cutting to woodworking. By examining the advantages these materials offer, we can better appreciate their crucial contribution to advancing manufacturing technologies in today's competitive landscape.
Cemented carbide inserts are essential tools in modern manufacturing, particularly in machining processes that require high precision and durability. These inserts typically consist of tungsten carbide (WC) and cobalt (Co), creating a composite material known for its hardness and strength. The standard composition involves about 88 wt% WC and 12 wt% Co, which enhances wear resistance and toughness, making them ideal for various applications ranging from metal cutting to drilling.
Recent advancements in additive manufacturing have opened new avenues for the development of cemented carbide inserts. By employing laser-based additive manufacturing combined with substrate preheating, manufacturers can produce customized inserts with intricate geometries that traditional methods cannot achieve. The use of powder bed fusion (PBF) technology facilitates precise control over the microstructure and mechanical properties of the inserts, leading to enhanced performance in machining applications. Reports indicate that these innovative methods improve production flexibility and reduce lead times, providing manufacturers with tailored solutions that meet specific operational requirements.
Cemented carbide inserts are essential tools in modern manufacturing, particularly in machining processes such as turning, milling, and drilling. These inserts are composed of tungsten carbide grains held together by a binder, usually cobalt, which provides exceptional durability and resistance to wear. According to a report from Grand View Research, the cemented carbide market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.1% from 2021 to 2028, highlighting the increasing demand for these materials in various industries.
One significant advantage of using cemented carbide inserts in manufacturing is their ability to retain cutting edges at high temperatures, reducing the frequency of tool replacements. This not only maximizes operational efficiency but also minimizes downtime, which is vital for maintaining productivity. Furthermore, their superior hardness means that they can cut through tough materials more effectively, leading to enhanced surface finishes and tighter tolerances. A study published in the Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering found that incorporating cemented carbide inserts improved machining performance by up to 30%, illustrating their critical role in enhancing manufacturing processes.
Tip: When selecting cemented carbide inserts, consider the specific material properties required for your machining application to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Additionally, regular monitoring of insert wear can help in choosing the right replacement schedule to maximize tool life.
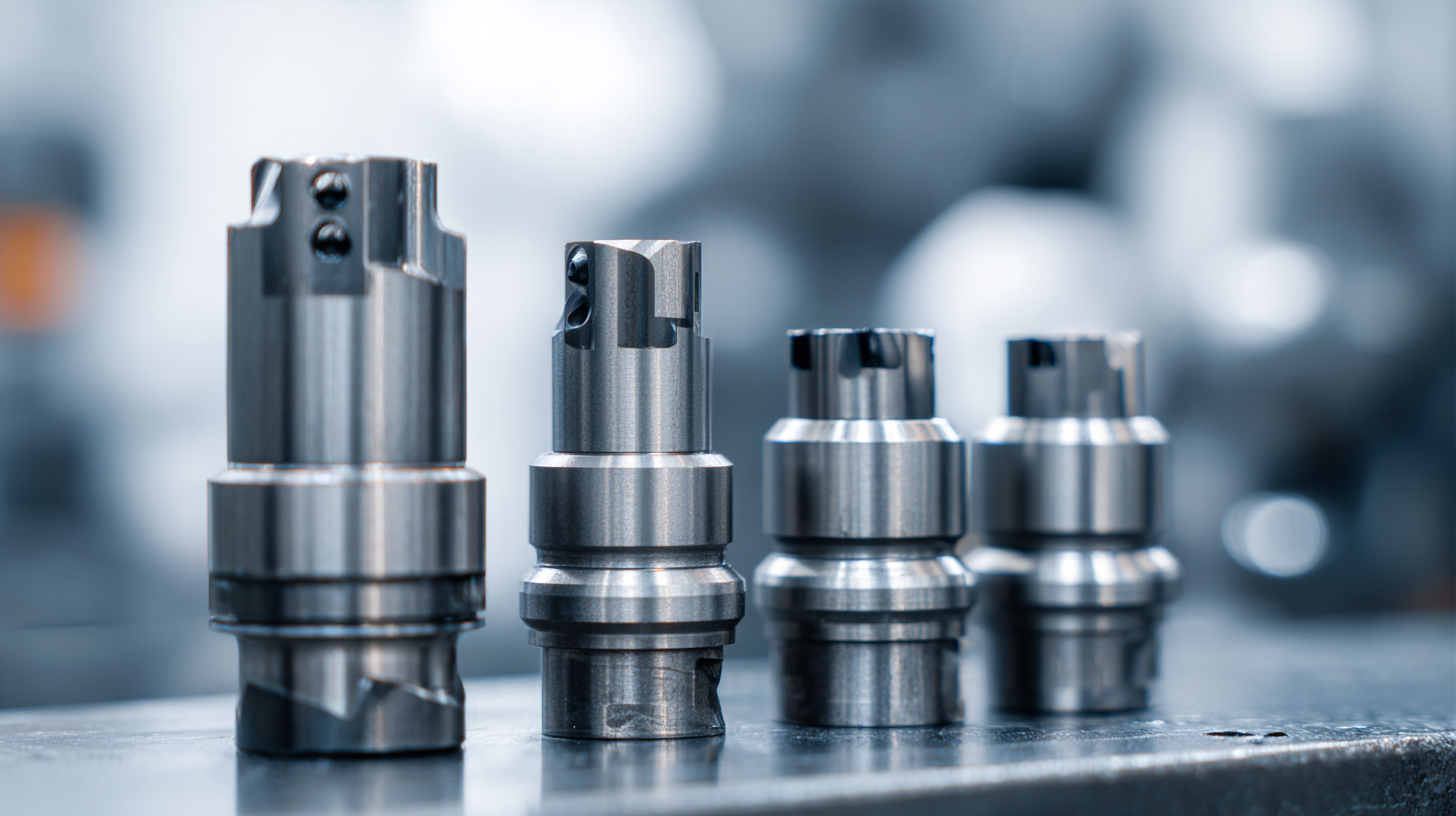
Cemented carbide inserts are critical components in modern manufacturing, known for their durability and resistance to wear. They are extensively used across various industries, from automotive and aerospace to metalworking and mining. The primary applications of these inserts include cutting tools for drilling, milling, and turning operations, where precision and efficiency are paramount. The robust characteristics of cemented carbide make them ideal for shaping and machining materials that would wear down lesser tools quickly.
In the automotive sector, cemented carbide inserts are employed in the production of engine components, while in the aerospace industry, they help manufacture critical parts that require high strength and reliability. The mining industry also benefits greatly from these tools, where cemented carbide inserts are used for drilling and excavation due to their exceptional hardness. As industries continue to demand higher efficiency and longer tool life, the application of cemented carbide inserts will undoubtedly expand, contributing significantly to advancements in manufacturing technologies.
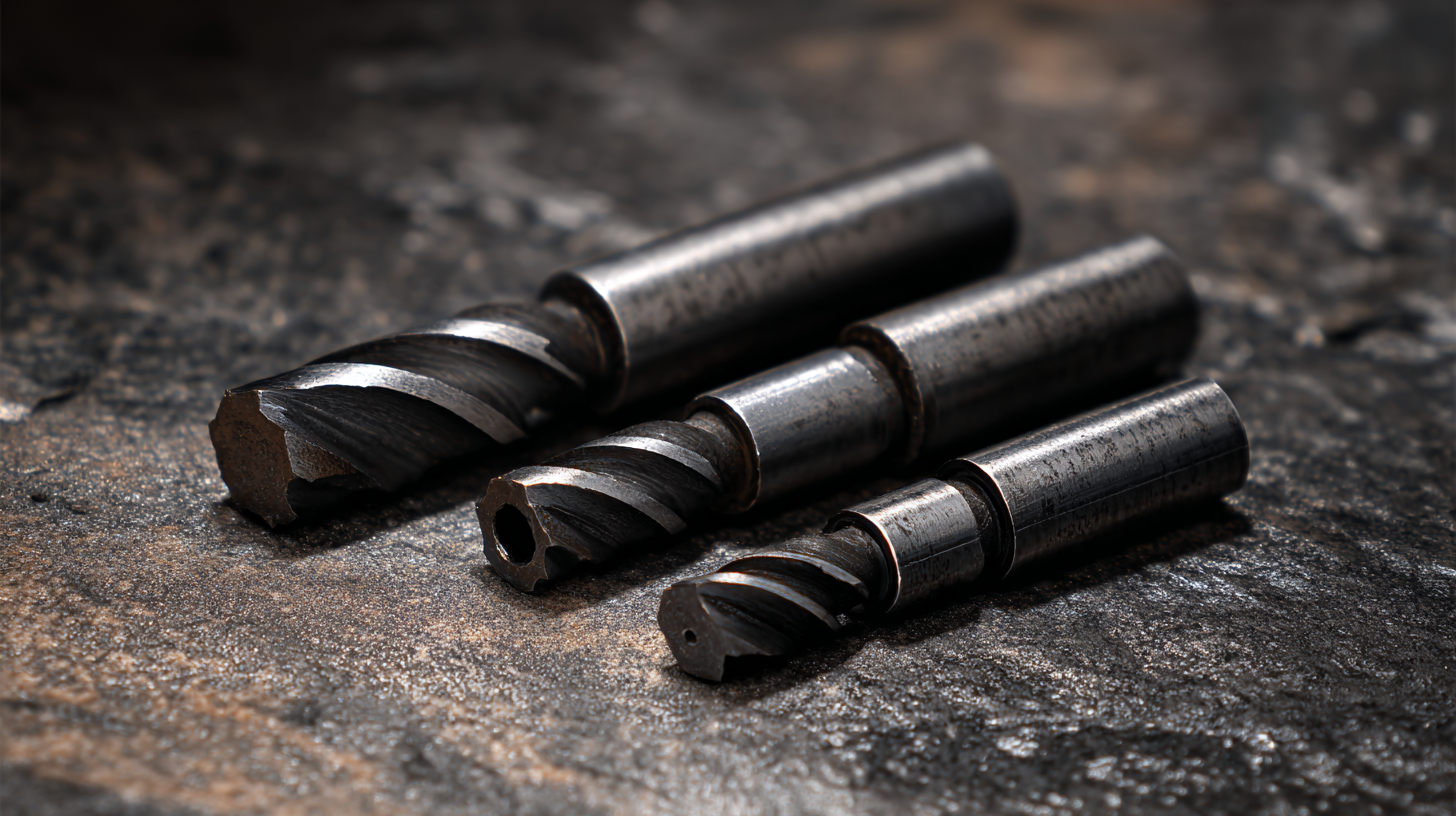 Cemented carbide inserts are renowned in manufacturing for their exceptional hardness and wear resistance. When compared to other cutting tool materials, such as high-speed steel (HSS) or ceramic, cemented carbide stands out particularly due to its ability to withstand high cutting temperatures and maintain sharpness over prolonged use. The unique composition, which typically includes tungsten carbide and cobalt, enables cemented carbide inserts to perform efficiently in high-speed machining operations, making them a preferred choice in industries that require precision and durability.
Cemented carbide inserts are renowned in manufacturing for their exceptional hardness and wear resistance. When compared to other cutting tool materials, such as high-speed steel (HSS) or ceramic, cemented carbide stands out particularly due to its ability to withstand high cutting temperatures and maintain sharpness over prolonged use. The unique composition, which typically includes tungsten carbide and cobalt, enables cemented carbide inserts to perform efficiently in high-speed machining operations, making them a preferred choice in industries that require precision and durability.
In contrast, while HSS tools are easier to re-sharpen and are more cost-effective for low-speed applications, they lack the thermal stability and hardness necessary for demanding conditions. Ceramic tools, on the other hand, are highly rigid and wear-resistant, but they can be brittle and prone to chipping under substantial force. Ultimately, cemented carbide inserts offer a balanced combination of toughness and performance, positioning them as a superior choice for modern manufacturing applications, where efficiency and precision are paramount.
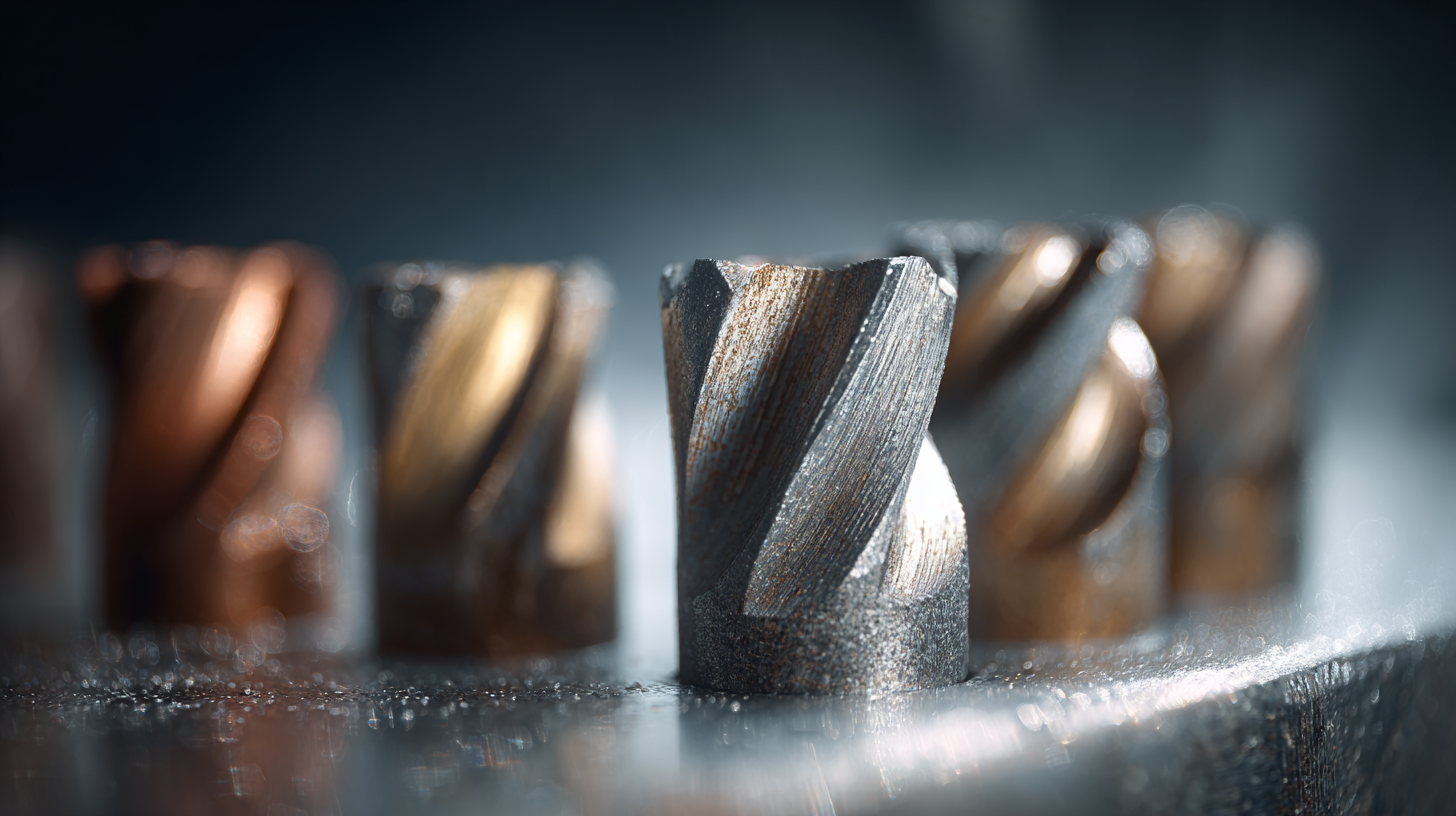 Cemented carbide inserts are at the forefront of modern manufacturing, particularly in the machining of difficult materials where precision and durability are paramount. As industries increasingly demand higher performance tools, the innovation within cemented carbide technology is growing rapidly. The latest advancements are focused on enhancing machinability through improved cooling and lubrication techniques. These developments address the challenges faced by manufacturers to increase efficiency and tool life while reducing production costs.
Cemented carbide inserts are at the forefront of modern manufacturing, particularly in the machining of difficult materials where precision and durability are paramount. As industries increasingly demand higher performance tools, the innovation within cemented carbide technology is growing rapidly. The latest advancements are focused on enhancing machinability through improved cooling and lubrication techniques. These developments address the challenges faced by manufacturers to increase efficiency and tool life while reducing production costs.
Looking ahead, the cemented carbide insert market is poised for significant change driven by technological advancements. Automation and digitalization are reshaping manufacturing processes, streamlining operations and enabling real-time data analysis for improved decision-making. Furthermore, the push for sustainability has opened new avenues in carbide recycling, enhancing profitability and contributing to a circular economy. Increasing investments in these areas suggest that future innovations will not only focus on performance but also on environmental responsibility, making cemented carbide an even more attractive option for modern manufacturing needs.